
Published: November 22, 2025 Reading Time: 22 minutes Last Updated: November 22, 2025
Introduction
The real estate market in 2025 presents a complex yet promising landscape for investors navigating post-pandemic normalization and evolving economic conditions. Despite ongoing uncertainties, real estate continues to offer unique advantages over traditional stock investments, including tangible asset ownership, powerful leverage opportunities, and substantial tax benefits that can generate wealth across market cycles.
Current market data reveals a sector in transition. Recent NAR reports show median home prices at $415,200 (up 2.1% year-over-year) with inventory improving to 4.4 months of supply as of October 2025. Mortgage rates have moderated from early 2025 peaks above 7%, now averaging 6.12% for 30-year fixed loans as of mid-November 2025, creating new opportunities for strategic investors.
This comprehensive guide addresses the needs of investors at all experience levels, from beginners making their first purchase to experienced investors expanding their portfolios. We’ll explore five distinct investment strategies with detailed analysis of current market conditions, financing options, and risk management approaches. Whether you have $100 or $100,000 to invest, understanding the 2025 real estate landscape will help you make informed decisions aligned with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
The 2025 Real Estate Market Landscape

Interest Rate Environment and Economic Factors
The Federal Reserve’s ongoing management of inflation continues to shape the 2025 real estate environment. After holding rates steady for several months at 4.25-4.50%, the Fed delivered quarter-point cuts in September and October 2025, bringing the federal funds rate to 4.00-4.25%. While a December meeting remains on the calendar, additional cuts are uncertain amid economic conditions.
Mortgage rates have responded to this environment by declining from early 2025 peaks. As of November 19, 2025, the average 30-year fixed-rate mortgage stands at 6.12%, down from over 7% in January 2025. The 15-year fixed-rate average is 5.37%, offering meaningful affordability improvements for qualified buyers. Most economists project continued gradual moderation toward the 5.5-6% range through 2026, though rates are unlikely to return to the historic lows of 2020-2021.
Housing Market Dynamics
Current housing prices reflect a market that has stabilized after previous volatility. NAR data from October 2025 shows median existing-home prices at $415,200, representing a 2.1% year-over-year increase—a marked deceleration from the double-digit appreciation of 2021-2022. Regional variations remain significant, with some Sun Belt markets experiencing corrections while stable Midwest markets show modest, consistent growth.
Inventory levels have improved substantially, reaching 4.4 months of supply nationally as of October 2025, up 0.4 months year-over-year. While still below the 6-month balance point that typically indicates a neutral market, this represents meaningful improvement from the severe shortages of 2021-2022 when inventory hit historic lows of 1.9 months.
Regional Market Variations
The 2025 market reveals clear geographic performance patterns:
- Sun Belt Markets: Cities like Phoenix, Las Vegas, and Austin continue experiencing price volatility but offer strong long-term growth potential driven by demographic migration trends and job growth in technology and healthcare sectors.
- Midwest Markets: Cleveland, St. Louis, Indianapolis, and Columbus demonstrate remarkable stability with consistent 2-4% appreciation and reliable cash flow metrics. The median home price in the Midwest is 22% below the national median, making it particularly attractive for investors.
- Coastal Markets: San Francisco, New York, and Boston show mixed performance, with luxury segments softening while mid-market properties maintain value due to limited supply and strong employment fundamentals.
Commercial vs. Residential Trends
The commercial real estate sector faces headwinds in 2025, particularly in office spaces where vacancy rates exceed 18% nationally due to persistent remote work trends. However, industrial properties and multifamily assets continue showing strength. Warehouse demand driven by e-commerce remains robust, while apartment occupancy rates hold above 94% in most markets, supported by demographic demand and housing affordability challenges.
Rent Growth and Economic Indicators
Rent growth has moderated from the double-digit increases of 2021-2022 but remains healthy at 3-4% annually on a national basis. Markets with strong job growth, particularly in technology, healthcare, and professional services sectors, continue outperforming with 5-7% rent growth. The national unemployment rate of 3.9% provides fundamental support for housing demand, though consumer confidence indicators suggest cautious optimism rather than exuberant market participation.
Strategy #1: Rental Properties
Single-Family Homes
Pros and Cons Analysis
Single-family rentals offer several compelling advantages for investors. These properties typically qualify for easier financing through conventional mortgages with down payments as low as 20-25% for investment properties. They attract broader tenant pools, including families seeking stability, and generally require lower maintenance costs per square foot compared to multifamily properties.
However, investors must carefully consider the challenges. Single-family rentals experience higher tenant turnover rates (typically 25-35% annually), creating vacancy periods and turnover costs. The single-point failure risk means one vacancy equals 100% vacancy for that property. Additionally, cash-on-cash returns may be lower due to higher purchase prices per unit compared to multifamily investments.
Deal Sourcing and Analysis
Successful investors employ multiple channels for finding properties:
- MLS Listings: The primary source for most investors, though competition remains fierce in desirable markets
- Off-Market Opportunities: Direct mail campaigns, wholesaler relationships, and networking with real estate professionals
- Foreclosure Auctions: Bank-owned properties (REO) and foreclosure sales requiring cash or hard money financing
- New Construction Pre-Sales: Opportunities in growing markets, particularly in suburban areas experiencing population growth
The traditional 1% rule (monthly rent should equal 1% of purchase price) remains a useful initial screening tool, though in current market conditions, achieving 0.8-0.9% may be more realistic in many markets due to elevated purchase prices.
Cash Flow Calculation Example
Property Investment Analysis:
- Purchase price: $350,000
- Down payment (25%): $87,500
- Mortgage payment (6.75%, 30-year): $1,798/month
- Property taxes: $350/month
- Insurance: $120/month
- Maintenance reserve: $200/month
- Vacancy reserve (5%): $125/month
- CapEx reserve: $150/month
- Property management (8%): $160/month
- Total monthly expenses: $2,903
- Market rent: $3,100/month
- Monthly cash flow: $197
- Cash-on-cash return: 2.7% annually
While a 2.7% cash-on-cash return may seem modest, this calculation doesn’t include appreciation, mortgage paydown, or tax benefits—all of which contribute to total returns. Conservative investors prioritize cash flow stability while building long-term wealth through these additional return components.
Best Markets for 2025
Mid-sized cities with diversified job bases and population growth offer the best balance of affordability and growth potential. Markets like Columbus OH, Raleigh NC, Nashville TN, and Indianapolis IN combine strong employment growth with reasonable entry prices and healthy rental demand. These markets typically show:
- Population growth of 1-2% annually
- Diverse employment base (not dependent on single industry)
- Strong education systems attracting families
- Median home prices below national average
- Rent-to-price ratios supporting positive cash flow
Multi-Family Properties (2-4 units)
Economies of Scale Benefits
Small multifamily properties offer significant advantages over single-family investments:
- Lower Maintenance Costs Per Unit: Sharing common systems like roofing, heating, and plumbing reduces per-unit expenses
- Reduced Vacancy Impact: One vacancy represents 25-50% revenue loss rather than 100%
- Financing Advantages: FHA loans available for owner-occupants with as little as 3.5% down
- Higher Overall Cash Flow Potential: Multiple income streams from a single property
House Hacking Strategy
The FHA house hacking approach allows investors to purchase 2-4 unit properties with only 3.5% down while occupying one unit. This strategy dramatically reduces personal housing expenses while building equity and generating rental income. For example, a $600,000 fourplex purchased with 3.5% down ($21,000) could potentially cover most or all of the mortgage through rental income from three units, effectively providing free housing while building wealth.
This strategy is particularly powerful for first-time investors with limited capital but stable income. The owner-occupancy requirement (typically one year) provides time to learn property management while benefiting from favorable financing terms.
Management Considerations
While managing 2-4 units requires more attention than single-family properties, it remains manageable for most investor-landlords. Essential systems include:
- Maintenance coordination and vendor relationships
- Tenant communication protocols and rent collection systems
- Financial tracking for multiple units
- Lease management and renewal processes
Many investors successfully self-manage small multifamily properties, saving the 8-10% management fees while maintaining direct relationships with tenants and control over property operations.
Short-Term Rentals (Airbnb/VRBO)
Income Potential and Challenges
Short-term rentals (STRs) can generate 2-3 times the revenue of traditional long-term rentals in suitable markets, but require significantly more active management and face increasing regulatory scrutiny. Successful STR operators typically achieve 50-70% occupancy rates with average daily rates 30-50% higher than equivalent monthly rents would provide.
The higher income potential comes with substantial operational requirements including guest communication, cleaning coordination, maintenance responsiveness, and dynamic pricing management. Many operators find that STR properties require 10-15 hours of management time per month, compared to 2-3 hours for long-term rentals.
Regulatory Environment
The regulatory landscape for short-term rentals has matured significantly by 2025. Many municipalities have implemented strict licensing requirements, occupancy taxes, and in some cases, outright bans in certain residential zones. Comprehensive regulatory due diligence is absolutely essential before purchasing a property for STR use.
Key regulatory considerations include:
- Local zoning ordinances and STR permit requirements
- Occupancy limits and safety requirements
- Transient occupancy tax obligations
- Homeowner association restrictions
- Parking and noise regulations
Location and Operational Considerations
The best STR locations combine strong tourist or business travel demand with favorable regulatory environments. Beyond location factors, successful STR operations require:
- Professional photography and compelling listing descriptions
- Dynamic pricing strategies using software like PriceLabs or Beyond Pricing
- Either dedicated self-management or premium management services (typically 20-30% of revenue)
- Higher-quality furnishings and amenities than long-term rentals
- Responsive guest communication (often 24/7 availability)

Strategy #2: Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
Public REITs
Market Performance and Characteristics
Publicly traded REITs offer investors liquid exposure to professionally managed real estate portfolios without the operational responsibilities of direct property ownership. These companies own and operate income-producing real estate across various sectors, from shopping centers to data centers, and are required to distribute at least 90% of taxable income as dividends.
Recent performance shows moderate returns with attractive income characteristics. Current dividend yields average 3.9-4.0% across the equity REIT sector, significantly higher than the S&P 500’s 1.24% dividend yield. Total return potential combines these dividends with capital appreciation, with J.P. Morgan Research projecting approximately 10% total returns for well-selected REIT investments through 2026.
Top Performing Sectors for 2025
Industrial REITs like Prologis (PLD) continue benefiting from e-commerce growth and supply chain restructuring. These REITs own and operate distribution centers and warehouses, with strong occupancy rates and growing rents driven by structural demand changes. Industrial REITs have shown approximately 11% NAV growth in 2025, supported by continued demand for logistics facilities.
Data Center REITs including Digital Realty (DLR) and Equinix (EQIX) capitalize on cloud computing and AI expansion. Data center REITs experienced impressive 21.3% FFO growth in 2025, driven by surging demand for AI infrastructure and cloud services. Digital Realty projects 6-7% core FFO growth for 2025, with improving occupancy rates expected to rise 100-200 basis points.
Healthcare REITs such as Welltower (WELL) demonstrate defensive characteristics with demographic tailwinds from an aging population. These REITs own senior housing, medical office buildings, and healthcare facilities, providing stable income with moderate growth potential.
Multifamily REITs like Equity Residential (EQR) offer stable income with moderate growth, benefiting from apartment occupancy rates above 94% in most markets and steady rent growth of 3-4% nationally.
Tax Considerations
REIT dividends typically receive less favorable tax treatment than qualified dividends from traditional stocks. Most REIT distributions are taxed as ordinary income at the investor’s marginal tax rate. However, a portion often constitutes return of capital, which reduces cost basis and defers taxes until the shares are sold. Additionally, qualified REIT dividends may qualify for the 20% pass-through deduction under Section 199A, providing some tax benefit for eligible investors.
Private REITs
Performance and Accessibility
Private REITs target higher returns (typically 8-12% annually) through access to less efficient market segments and value-add strategies not available to retail investors otherwise. Platforms like Fundrise and RealtyMogul have democratized access to private real estate investments, with minimum investments ranging from $10 to $5,000 depending on the platform and offering type.
However, these investments sacrifice liquidity. Private REITs typically require 3-7 year hold periods with limited or no secondary market for selling shares before maturity. Redemption policies vary by platform, with some offering quarterly redemption windows subject to limitations.
Due Diligence Framework
Evaluating private REITs requires careful analysis of several critical factors:
- Sponsor Track Record: Historical performance, experience in target markets and property types, and alignment of interests with investors
- Fee Structure: Management fees, acquisition fees, disposition fees, and expense ratios that can significantly impact net returns
- Investment Strategy: Property types, geographic focus, value-add vs. core strategies, and leverage policies
- Redemption Policies: Liquidity options, redemption limits, and historical redemption fulfillment rates
- Historical Performance: Track record through full market cycles, not just recent strong periods
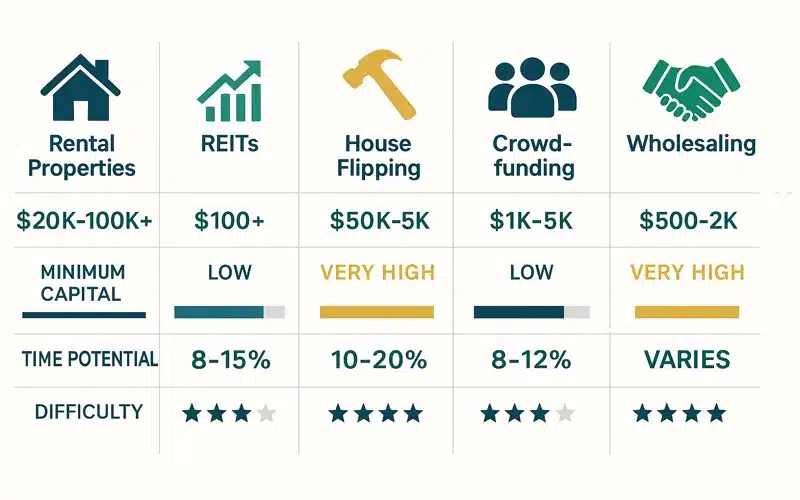
REIT vs Physical Property Comparison
| Factor | Physical Property | REITs |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Investment | $20,000-$100,000+ | $100+ (public) / $10-$5,000 (private) |
| Liquidity | Low (months to sell) | High (public) / Low (private) |
| Management | Active involvement required | Passive – professional management |
| Control | High – direct decision-making | Low – trust management team |
| Leverage | Available through mortgages | None at investor level |
| Tax Benefits | Depreciation, 1031 exchanges | Limited – ordinary income treatment |
| Cash Flow | Monthly potential | Quarterly dividends |
| Appreciation | Direct benefit | Indirect through share price |
| Diversification | Difficult and expensive | Instant across properties |
| Total Return Potential | 8-15%+ with active management | 7-12% with passive ownership |
Strategy #3: House Flipping
Market Conditions for 2025
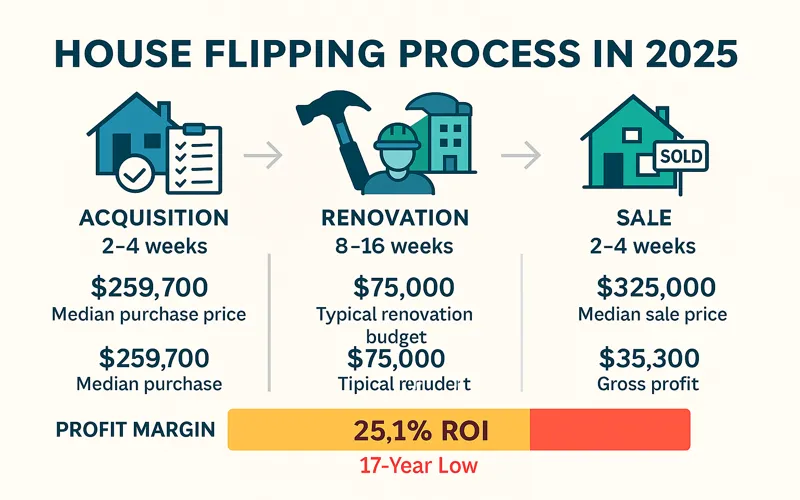
The house flipping environment in 2025 requires significantly more sophistication than during the easy-money years of 2020-2021. ATTOM Data Solutions reports that the typical flipped home in Q2 2025 generated a gross profit of $65,300 (down 13.6% year-over-year) with a 25.1% return on investment before expenses—the lowest margin since 2008.
Flipping profits have been steadily declining for over a decade. In fall 2012, typical returns exceeded 60%. The current environment demands genuine value creation rather than relying on market momentum. Successful flippers must focus on properties requiring specific improvements and develop efficient renovation systems with reliable contractor relationships.
The median purchase price for flipped properties hit a record $259,700 in Q2 2025, while median resale prices held at $325,000. This squeeze between rising acquisition costs and stable resale values has compressed margins significantly, requiring more careful deal selection and execution.
Financial Requirements and Analysis
Capital Requirements
Successful flipping typically requires $50,000-$150,000+ in available capital, allocated across:
- Acquisition Costs: Down payment, earnest money deposits, and closing costs
- Renovation Funding: Materials and labor costs for improvements
- Carrying Costs: Loan payments, property taxes, insurance, and utilities during the hold period
- Contingency Reserves: 15-20% of renovation budget for unexpected issues and cost overruns
The 70% Rule in Practice
The standard flipping guideline suggests: Maximum Offer = (ARV × 0.70) – Repair Costs
Example Analysis:
Property with $500,000 After Repair Value (ARV) needing $75,000 in repairs:
Maximum Offer = ($500,000 × 0.70) – $75,000 = $275,000
In competitive markets, investors may need to adjust to 75-80% of ARV to secure deals, but this significantly increases risk exposure and reduces potential profits. The 70% rule provides necessary cushion for unexpected costs, market changes during the hold period, and adequate profit margin.
Operational Execution
Timeline Management
Successful flips typically complete within 3-6 months total, with the following breakdown:
- 2-4 weeks: Acquisition and due diligence, including inspections and contractor bids
- 8-16 weeks: Renovations, varying based on scope of work
- 2-4 weeks: Sale and closing process
Extended timelines erode profits through carrying costs. Each additional month holding a property costs thousands in loan payments, taxes, insurance, and utilities. Successful flippers develop systems to minimize holding time while maintaining quality renovations.
Profit Margin Analysis
After accounting for all costs including renovations (typically 20-33% of ARV), carrying costs, selling expenses, and taxes, average net profits range from $20,000-$60,000 per project. This represents approximately 10-20% of ARV in current market conditions, down substantially from historical norms.
Higher-margin projects often involve complex renovations that less experienced investors avoid, or unique market opportunities requiring specialized knowledge. Building expertise in specific property types or renovation categories can provide competitive advantages.
Tax and Risk Considerations
Tax Implications
Flipped properties generate short-term capital gains taxed at ordinary income rates (up to 37% federal plus state taxes). This tax treatment significantly impacts net returns. Investors who qualify as real estate professionals under IRS criteria may deduct losses against other income, though this requires meeting specific requirements including 750 hours annually spent in real estate activities.
Common Mistakes
Learning from others’ mistakes can save tens of thousands of dollars:
- Underestimating Repair Costs: Lacking detailed contractor bids and adequate contingency reserves (minimum 15-20%)
- Overestimating ARV: Emotional attachment to renovations or insufficient comparable sales analysis
- Inadequate Contractor Vetting: Not checking licenses, insurance, references, and previous work quality
- Insufficient Contingency Planning: No buffer for delays, cost overruns, or market changes
- Poor Market Timing: Buying near market peaks or holding through seasonal slow periods
Strategy #4: Real Estate Crowdfunding
Platform Comparison and Selection
Real estate crowdfunding has matured into a legitimate asset class, with platforms serving different investor segments and offering varying levels of access, minimum investments, and investment types:
| Platform | Minimum Investment | Focus | Investor Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fundrise | $10 | Diversified portfolios | Non-accredited accepted |
| RealtyMogul | $5,000 | Individual deals | Non-accredited for REITs |
| CrowdStreet | $25,000 | Commercial projects | Accredited only |
| Yieldstreet | $10,000 | Diverse alternatives | Accredited preferred |
Investment Performance and Risks
Historical Returns
Crowdfunding platforms typically target 8-12% annual returns, though actual performance varies significantly by project type, location, sponsor quality, and market conditions. Debt investments generally offer lower returns (7-9%) with higher security through senior position in the capital stack, while equity investments target higher returns (10-15%+) with increased risk exposure.
It’s crucial to understand that projected returns and actual returns often differ. Platform track records should be evaluated across full market cycles, not just favorable recent periods. Some platforms have experienced project failures, defaults, or delays that significantly impacted investor returns.
Risk Assessment
Key risks requiring careful consideration include:
- Illiquidity Risk: Typical 3-7 year hold periods with extremely limited secondary markets for early exit
- Platform Risk: Dependency on sponsor competence, alignment of interests, and platform operational quality
- Project-Specific Risks: Construction delays, leasing shortfalls, market changes, and unforeseen costs
- Concentration Risk: Without adequate diversification across multiple projects, single investment failures can significantly impact overall returns
- Regulatory Risk: Changing regulations around crowdfunding could impact platform operations or investment structures
Investor Qualifications and Strategies
Accredited vs Non-Accredited Investors
SEC regulations create different access levels based on investor accreditation status. Accredited investors (net worth >$1M excluding primary residence or income >$200k individual/$300k joint) can access most crowdfunding opportunities. Non-accredited investors have more limited options but can still participate through Regulation A+ offerings on platforms like Fundrise, which provide access to diversified real estate portfolios.
Portfolio Construction
Successful crowdfunding investors typically employ these principles:
- Limited Allocation: Allocate only 5-15% of overall investment portfolio to real estate crowdfunding due to illiquidity
- Platform Diversification: Spread investments across multiple platforms to reduce platform-specific risks
- Project Type Diversity: Mix debt and equity investments, different property types, and various geographic markets
- Fee Structure Understanding: Carefully analyze all fees including acquisition fees, management fees, disposition fees, and carried interest
- Realistic Expectations: Maintain appropriate expectations about both returns and liquidity constraints
Strategy #5: Wholesaling
Business Model Overview
Wholesaling offers a low-capital entry point into real estate investing, focusing on contract assignment rather than property ownership. Wholesalers identify motivated sellers willing to sell below market value, negotiate purchase contracts, then assign those contracts to end buyers (typically rehabbers or landlords) for an assignment fee.
This strategy requires minimal capital compared to other real estate investments but demands significant time, marketing investment, and deal flow management. Success depends on building systems for lead generation, property analysis, and buyer network development.
Typical Financials
- Assignment Fees: $5,000-$15,000 per deal (varying by market and property value)
- Marketing Costs: $500-$2,000 monthly for direct mail, digital advertising, and lead generation
- Time Investment: 40+ hours weekly initially to build systems and deal flow
- Success Rate: Typically 1-3% of leads convert to closed deals, requiring substantial lead volume
Marketing and Lead Generation
Successful wholesalers employ multiple marketing channels to generate consistent deal flow:
- Direct Mail Campaigns: Targeted mailings to probate properties, pre-foreclosures, absentee owners, and other motivated seller lists
- Driving for Dollars: Identifying distressed properties through neighborhood canvassing
- Digital Marketing: Paid advertising on Google, Facebook, and specialized platforms targeting motivated sellers
- Networking: Building relationships with real estate agents, attorneys, other investors, and property managers for referrals
- Online Platforms: Using websites and landing pages to capture inbound leads from sellers researching options
Legal and Operational Considerations
Licensing Requirements
The legal status of wholesaling varies significantly by state. Some jurisdictions require real estate licenses for certain wholesaling activities, particularly when marketing properties you don’t own or have equitable interest in. Consult with a real estate attorney in your state to understand local regulations and ensure compliance.
Key legal considerations include:
- Proper contract language for assignment clauses
- Disclosure requirements to sellers about assignment intentions
- State-specific licensing laws
- Earnest money handling and escrow requirements
Ethical Considerations
Successful wholesalers focus on creating genuine value by solving problems for motivated sellers—not merely extracting value through information asymmetry. Ethical wholesaling practices include:
- Transparent communication about your business model and intentions
- Fair pricing that genuinely helps sellers in difficult situations
- Delivering on promises made during negotiations
- Building reputation for honesty and professionalism
Unethical practices damage reputation, limit referral opportunities, and can create legal liability. The most successful wholesalers build sustainable businesses through repeat referrals and strong reputations in their markets.
Financing Options Explained
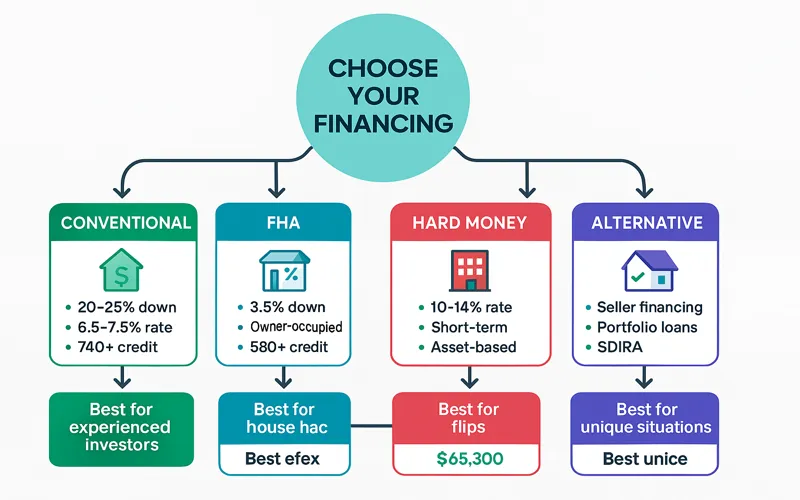
Conventional Mortgages
Current Market Conditions
Conventional investment property loans typically require 20-25% down payments with rates averaging 6.5-7.5% for borrowers with excellent credit (740+) as of November 2025. These rates are approximately 0.5-0.75% higher than owner-occupied loans due to increased lender risk.
Debt-to-income (DTI) ratios generally must remain below 45%, though some portfolio lenders offer more flexibility. Lenders increasingly scrutinize rental income claims, typically requiring lease agreements or appraisal rent schedules to verify income potential.
Lender Requirements
- Credit Scores: Minimum 680-740 for investment properties (higher scores receive better rates)
- Cash Reserves: 6-12 months of mortgage payments required in liquid reserves
- Property Coverage: Debt service coverage ratio typically 1.2x minimum (rental income must exceed mortgage payment by 20%)
- Experience: Some lenders require previous landlord experience for multiple properties
Government-Backed Loans
FHA Loans for House Hacking
FHA loans allow 3.5% down payments on 1-4 unit properties with owner-occupancy requirements. The mortgage insurance premium (1.75% upfront plus 0.85% annually for most borrowers) increases overall costs but enables much lower initial capital requirements.
This financing option is particularly powerful for house hacking strategies, where rental income from additional units can cover most or all of the mortgage payment, providing free or low-cost housing while building equity.
Key FHA Requirements:
- Owner must occupy one unit as primary residence for at least one year
- Credit score minimums of 580 for 3.5% down (500-579 requires 10% down)
- DTI ratios typically capped at 43-50%
- Property must meet FHA minimum property standards
VA Loans
Eligible veterans can purchase 1-4 unit properties with no down payment through VA loans, subject to entitlement limits and occupancy requirements. This represents one of the most powerful wealth-building opportunities available to qualifying service members and veterans.
VA loans offer competitive interest rates, no mortgage insurance requirements, and flexible credit standards. However, the VA funding fee (typically 2.15-3.3% depending on service type and down payment) adds to upfront costs, though it can be financed into the loan amount.
Alternative Financing Options
Portfolio Loans
Local banks and credit unions that portfolio their loans (keep them on their own books rather than selling to Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac) often offer more flexible terms. These may include:
- Non-standard property types (mixed-use, unique properties)
- Higher DTI ratios for strong borrowers
- Shorter amortization periods (15-20 years typical)
- Relationship-based lending for existing customers
Rates are typically 0.25-0.75% higher than conventional loans, but the flexibility can make deals possible that wouldn’t qualify for standard financing.
Hard Money Loans
Short-term (6-24 month) loans at higher interest rates (10-14%) with points (2-4% of loan amount) are used primarily for flips and quick acquisitions where traditional financing isn’t feasible. Hard money lenders focus on property value and exit strategy rather than borrower credit and income.
These loans are unsuitable for long-term holdings due to high costs but provide critical bridge financing for time-sensitive opportunities or properties requiring extensive renovation before they qualify for conventional financing.
Seller Financing
Negotiating directly with property sellers can create flexible terms including:
- Lower down payments (5-15% vs. 20-25%)
- Interest-only periods reducing early cash flow requirements
- Graduated payment structures
- Balloon payments after several years
This strategy works best with motivated sellers who have significant equity, particularly those seeking installment sale tax treatment or passive income streams. Seller financing is more common in slower markets or with properties that have been listed for extended periods.
Self-Directed IRA
Using retirement funds for real estate investing allows tax-advantaged growth but comes with complex rules prohibiting self-dealing and requiring proper administration. This approach works best for hands-off strategies like:
- REIT investments
- Real estate crowdfunding
- Private lending to other investors
- Turnkey rental properties with third-party management
Direct property ownership in a self-directed IRA creates complications around repairs, management, and ensuring no prohibited transactions occur. Consult with specialized self-directed IRA custodians and tax professionals before pursuing this strategy.
Due Diligence Checklist
Property-Specific Analysis
Physical Inspection
Never skip professional inspections. A comprehensive inspection by qualified professionals can identify structural, mechanical, and environmental issues not apparent during casual viewing. Budget $400-$800 for thorough inspections, plus additional costs for specialized inspections when warranted:
- General home inspection covering structure, systems, and major components
- Pest inspection (termites, carpenter ants, rodents)
- Radon testing in high-risk areas
- Mold inspection if moisture issues are suspected
- Foundation specialist for structural concerns
- Chimney inspection for properties with fireplaces
- Sewer scope inspection for older properties
Financial Verification
For income-producing properties, verify all financial claims:
- Rent Rolls: Current rents, lease terms, security deposits, and tenant payment history
- Operating Expenses: Verify through utility bills, tax records, insurance policies, and maintenance records
- Capital Expenditure Assessment: Age and condition of roof, HVAC, water heater, appliances, and other major systems
- Comparable Rent Analysis: Verify market positioning through competing property analysis and property manager consultations
Market and Legal Considerations
Neighborhood Analysis
- Crime Statistics: Current rates and trend analysis using local police department data
- School Quality: District ratings and boundaries (major factor for family tenants)
- Amenity Access: Walkability scores, proximity to employment, shopping, and transportation
- Development Plans: Zoning changes, new construction, and infrastructure improvements that could impact values
- Economic Indicators: Local employment trends, major employers, and population growth patterns
Legal and Regulatory Review
- Title Search: Review commitment thoroughly for liens, easements, and encumbrances
- Zoning Verification: Confirm permitted uses and any restrictions on rental use
- HOA Restrictions: Review covenants, conditions, and restrictions (CC&Rs) for rental limitations, maintenance requirements, and financial health
- Environmental Concerns: Flood zones, soil stability, lead paint (pre-1978 homes), asbestos, and contamination history
- Permit History: Verify all renovations were properly permitted to avoid future complications
Investment Performance Validation
Comparable Sales Analysis
Review recent sales (last 3-6 months) of similar properties in the immediate area. Adjust for differences in:
- Square footage and lot size
- Bedrooms and bathrooms
- Condition and updates
- Location within neighborhood
- Special features (garage, pool, views)
Rent Estimates
Consult multiple local property managers for realistic rent projections rather than relying on optimistic online estimates. Verify actual rental performance through:
- MLS rental listings for competing properties
- Craigslist and Zillow rental listings
- Property manager market surveys
- Days on market analysis for similar rentals
Tax Benefits & Strategies
Deduction Strategies
Depreciation Benefits
Residential rental properties depreciate over 27.5 years for tax purposes, creating paper losses that can offset actual rental income even when cash flow is positive. For a $400,000 property with $100,000 allocated to land value, this generates approximately $10,909 in annual depreciation deductions ($300,000 building value ÷ 27.5 years).
This powerful tax benefit allows investors to show accounting losses while generating positive cash flow, deferring income taxes on rental income. Cost segregation studies can accelerate depreciation on certain components, though this typically makes sense only for larger properties or portfolios.
Expense Deductions
Rental property owners can deduct ordinary and necessary expenses including:
- Mortgage Interest: Interest portion of loan payments (principal is not deductible)
- Property Taxes: Annual property taxes (though subject to $10,000 SALT deduction limit for itemized deductions)
- Operating Expenses: Maintenance, repairs, utilities, property management fees, insurance, and advertising
- Travel Expenses: Mileage and travel costs for property visits (with proper documentation)
- Professional Services: Legal fees, accounting services, property management
- Home Office: If you maintain a dedicated space for rental property management
Wealth Building Strategies
1031 Exchanges
Section 1031 exchanges allow deferring capital gains taxes indefinitely by reinvesting proceeds into like-kind properties. This powerful wealth-building tool enables portfolio growth through tax-deferred compounding. Strict timing rules must be followed:
- 45-Day Identification Period: Must identify potential replacement properties within 45 days of selling relinquished property
- 180-Day Exchange Period: Must close on replacement property within 180 days of selling relinquished property
- Qualified Intermediary Required: Cannot take possession of sale proceeds; must use qualified intermediary
- Equal or Greater Value: Replacement property must be equal or greater value to defer all capital gains
Opportunity Zones
Investments in designated Opportunity Zones offer potential capital gains tax reductions and elimination for long-term holdings. However, program benefits are scheduled to phase out, with optimal tax benefits requiring investments made before December 31, 2026. Consult with tax professionals about current benefits and requirements.
Real Estate Professional Status
Qualifying as a real estate professional under IRS criteria unlocks significant deductions, including ability to offset W-2 income with real estate losses. Requirements include:
- More than 750 hours annually in real estate activities
- Majority of working time spent in real estate (more than any other occupation)
- Material participation in rental activities
- Proper time tracking and documentation
This status provides powerful tax benefits but requires substantial time commitment and careful documentation. It’s most beneficial for full-time investors or those transitioning from W-2 employment to real estate focus.
Implementation Considerations
CPA vs DIY Approach
Determining when to hire professional tax help versus DIY preparation depends on portfolio complexity. Professional guidance becomes increasingly worthwhile for:
- Multiple properties or complex entity structures (LLCs, partnerships)
- 1031 exchanges or opportunity zone investments
- Qualification attempts for real estate professional status
- State tax optimization across multiple jurisdictions
- Cost segregation studies and advanced depreciation strategies
Budget $500-$2,000+ annually for competent real estate CPA services. The tax savings typically far exceed the professional fees for investors with multiple properties or complex situations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Financial Pitfalls
Underestimating Costs
Always include a 20% buffer beyond contractor estimates for unexpected issues. Common underestimations include:
- Repair and Renovation Costs: Hidden issues discovered during work (foundation, electrical, plumbing)
- Carrying Costs: Extended vacancy periods, financing costs during renovations
- Capital Expenditure Requirements: Roof, HVAC, water heater, and system replacements
- Administrative Expenses: Property management, accounting, legal services, and insurance
Overleveraging
Excessive debt creates vulnerability to market downturns or personal financial setbacks. Conservative investors maintain:
- Overall loan-to-value ratios below 75% across portfolio
- Cash reserves covering 6+ months of all property expenses
- Debt service coverage ratios above 1.25x (rental income exceeds debt service by 25%)
- Personal emergency fund separate from investment reserves
Negative Cash Flow Trap
Properties that consume rather than generate monthly cash create constant financial pressure and severely limit portfolio scalability. The “appreciation speculation” strategy—buying properties with negative cash flow betting on appreciation—rarely succeeds over multiple market cycles.
While short-term negative cash flow might be acceptable in exceptional circumstances (strong appreciation market, planned rent increases, temporary vacancy), sustained negative cash flow indicates problematic property selection or market conditions.
Operational Errors
Inadequate Tenant Screening
Comprehensive background, credit, and reference checks prevent problematic tenancies that can cost thousands in eviction costs, legal fees, and property damage. Standard screening should include:
- Credit checks with minimum score requirements (typically 620+)
- Criminal background checks (while complying with Fair Housing requirements)
- Rental history verification with previous landlords
- Income verification (typically 3x monthly rent minimum)
- Employment verification
- Reference checks
The cost of thorough screening ($50-$100) is minimal compared to potential costs of problem tenants ($5,000-$20,000+ in lost rent, eviction costs, and damages).
Legal Compliance Gaps
Not understanding landlord-tenant laws creates significant liability exposure. Key areas requiring knowledge include:
- Security Deposit Handling: State-specific limits, accounting requirements, and return timelines
- Eviction Process: Proper notice requirements, court procedures, and prohibited self-help evictions
- Habitability Requirements: Mandatory repairs, response timelines, and tenant rights
- Fair Housing Compliance: Protected classes, prohibited discrimination, reasonable accommodations
- Lead Paint Disclosure: Required for pre-1978 properties
Team Building Neglect
Successful real estate investors build competent teams rather than attempting to handle everything themselves. Essential team members include:
- Real Estate Agent: Investment-experienced agent understanding investor needs and analysis
- Mortgage Broker: Access to multiple lenders and investment property loan options
- Real Estate Attorney: Contract review, entity formation, landlord-tenant issues
- CPA: Real estate expertise, tax planning, and return preparation
- Insurance Agent: Understanding landlord policies, liability coverage, and risk management
- Contractors: Reliable, licensed contractors for maintenance and renovations
- Property Manager: Professional management as portfolio scales
Getting Started in 2025
Education Foundation
Learning Pathways
Build knowledge systematically through multiple resources:
- Books: “The Book on Rental Property Investing” by Brandon Turner, “The Millionaire Real Estate Investor” by Gary Keller, “What Every Real Estate Investor Needs to Know About Cash Flow” by Frank Gallinelli
- Podcasts: BiggerPockets Real Estate Podcast, Real Estate Today, The Real Estate Guys Radio Show, Best Real Estate Investing Advice Ever
- Courses and Training: Local real estate investment associations (REIAs), CCIM fundamentals, online courses from established investors
- Networking: Join local REIA groups, attend real estate meetups, connect with experienced investors as mentors
Market Research
Develop deep knowledge of 2-3 target markets through systematic research:
- MLS Data Analysis: Track pricing trends, days on market, inventory levels, and sold vs. list price ratios
- Economic Development Research: Major employers, job growth projections, population trends, and development plans
- Networking: Connect with local real estate agents, property managers, contractors, and other investors
- Physical Market Knowledge: Drive neighborhoods, attend open houses, understand neighborhood characteristics
- Rental Market Analysis: Monitor rental listings, vacancy rates, average rents, and tenant demand indicators
Capital Development
Funding Strategies
- Personal Savings: Automated investment plans directing portion of income to real estate fund
- Home Equity: HELOCs or cash-out refinances on primary residence (use cautiously)
- Retirement Funds: Self-directed IRA structures for appropriate investments
- Partner Capital: Joint ventures with friends, family, or other investors
- Private Money: Relationships with individual lenders willing to finance deals
Capital Allocation
Beginner investors should target $10,000-$50,000 as an ideal starting capital base, allocated across:
- Down payment and acquisition costs (largest component)
- Initial repairs and improvements
- Cash reserves (6+ months of expenses minimum)
- Education budget (courses, books, networking events)
- Due diligence budget (inspections, professional consultations)
Implementation Framework
Strategy Selection
Choose investment approaches aligned with your specific resources:
- Limited Capital ($100-$10,000): REITs, crowdfunding platforms, wholesaling, partnerships
- Moderate Capital ($10,000-$50,000): House hacking with FHA financing, small single-family rentals in cash flow markets
- Substantial Capital ($50,000+): Traditional rentals, small multifamily, house flipping, commercial properties
Consider time availability, risk tolerance, desired involvement level, and learning curve when selecting strategies. Most investors find success starting with one strategy and expanding to others as experience and capital grow.
Deal Analysis Discipline
Practice analyzing 100 deals to develop the discernment that separates successful investors from amateurs. Develop systematic evaluation criteria including:
- Minimum cash-on-cash return thresholds (typically 6-8%)
- Capitalization rate requirements for market
- Neighborhood quality standards (crime rates, schools, employment)
- Property condition assessment protocols
- Maximum price per square foot or price-to-rent ratios
Document your analysis process, including deals rejected and reasons why. This creates a valuable reference for future decision-making and helps refine investment criteria over time.
Progressive Scaling
Begin with one property or REIT investment to gain experience before aggressive scaling. Benefits of measured growth include:
- Learning operational realities with manageable risk exposure
- Developing systems and processes that can be replicated
- Building team relationships (contractors, managers, lenders)
- Understanding personal capacity and interest in property management
- Allowing time to adjust strategy based on market performance
Expand deliberately based on demonstrated competence, system development, and market opportunities rather than arbitrary timelines. Successful long-term investors prioritize quality over quantity, focusing on properties that meet strict investment criteria.
Conclusion
Real estate investing remains a powerful wealth-building vehicle in 2025, offering multiple pathways to financial independence regardless of your starting point. The current market environment—with stabilized prices after previous volatility, improving inventory levels, and moderating mortgage rates—creates opportunities for informed, disciplined investors willing to do comprehensive due diligence.
Success in real estate investing requires selecting strategies aligned with your specific resources and goals, conducting thorough analysis of each opportunity, and building systems that allow for sustainable portfolio growth. Whether you begin with a REIT investment requiring just $100, utilize house hacking to acquire your first rental property, or start a wholesaling business with sweat equity, taking that first step positions you to benefit from the unique advantages that real estate offers.
The key differentiators between successful and unsuccessful real estate investors aren’t luck or timing—they’re education, discipline, and systematic execution. Markets will continue cycling through periods of growth and correction. Investors who maintain consistent standards, adequate reserves, and long-term perspective will build substantial wealth regardless of short-term market fluctuations.
For those seeking additional investment guidance, explore our comprehensive resources on overall investment strategies for 2025, creating passive income streams, and navigating broader market conditions.
Your assignment this week: Select one strategy from this guide to research in greater depth. Take one concrete action toward implementation—whether opening a brokerage account for REIT investing, analyzing a specific rental property in your target market, or connecting with a potential team member like a real estate agent or property manager. Small, consistent actions compound into significant results over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much money do I need to start real estate investing in 2025?
You can begin real estate investing with as little as $10-$100 through REIT investments on platforms like Fundrise, or $10,000-$50,000 for rental properties using conventional financing with 20-25% down payments. House hacking with FHA financing requires just 3.5% down, potentially allowing property acquisition for $15,000-$25,000 including closing costs and reserves. The strategy should match your available capital—there’s no universal “right” amount to start. Creative financing options like partnerships, seller financing, or wholesaling can further reduce initial capital requirements while you build experience and resources.
Is now a good time to invest in real estate in November 2025?
Current market conditions present both challenges and opportunities. Mortgage rates have moderated to approximately 6.12% for 30-year fixed loans (down from over 7% in January 2025), improving affordability compared to early 2025. Home prices have stabilized with modest 2-3% year-over-year appreciation, while inventory has improved to 4.4 months of supply. Rather than attempting to time the market perfectly, focus on finding fundamentally sound investments that generate positive cash flow and meet your investment criteria within current economic conditions. Time in market historically proves more important than market timing for long-term real estate success.
Should I invest in real estate locally or out-of-state?
Local investing offers significant advantages including direct market knowledge, ability to personally inspect properties, and easier management oversight. However, out-of-state investing provides access to higher-yield markets with better cash flow metrics than expensive local markets. Beginners typically benefit from starting locally while building knowledge of other markets for future diversification. Successful out-of-state investing requires building strong local teams (property managers, contractors, real estate agents), implementing systematic due diligence processes, and accepting reduced control compared to local investments. Many successful investors ultimately maintain portfolios in both local and remote markets.
What’s better: physical rental properties or REITs?
The superior choice depends entirely on your goals, resources, and preferences. Physical rental properties offer greater control, leverage benefits through mortgages, and powerful tax advantages like depreciation and 1031 exchanges. However, they require active management, higher minimum capital ($20,000-$100,000+), and limited liquidity. REITs provide instant diversification, professional management, high liquidity (for public REITs), and low minimum investments ($100+), but offer less control and different tax treatment (ordinary income vs. capital gains). Many successful investors ultimately incorporate both into diversified portfolios, using REITs for passive exposure and physical properties for control and tax advantages.
How do I find good real estate deals in a competitive market?
Finding deals in competitive markets requires multiple approaches and persistence. Build relationships with real estate agents who understand investor needs and criteria. Implement direct marketing campaigns targeting motivated sellers (probate, pre-foreclosure, absentee owners). Focus on off-market sourcing through networking with wholesalers and other investors. In current conditions, properties requiring cosmetic improvements or having unique situations (estate sales, divorce, job relocation) often present better opportunities than turnkey properties competing with retail buyers. Develop clear investment criteria and maintain discipline—analyzing 100+ properties to find one good deal is normal. Being prepared to move quickly when opportunities arise (pre-approved financing, available capital, strong team) separates successful investors from those who miss good deals.
Do I need an LLC for my rental properties?
LLCs provide liability protection and potential estate planning benefits but can complicate financing (many lenders won’t finance LLC-owned properties) and add administrative complexity with annual fees and separate bookkeeping requirements. Beginning investors often hold initial properties in personal names with adequate landlord insurance while planning entity structures for future portfolio growth. As portfolios expand or risk exposure increases, entity structuring becomes increasingly important. Consult with real estate-focused attorneys and CPAs familiar with your specific situation, state laws, and investment goals to determine optimal structure. Insurance (landlord policies, umbrella coverage) often provides substantial liability protection at lower cost and complexity than LLC formation for smaller portfolios.
What are the biggest risks in real estate investing?
Key risks include liquidity constraints (difficulty quickly accessing invested capital), market cycles that can reduce property values, interest rate changes affecting financing costs and property values, problematic tenants creating income disruption and property damage, unexpected major repairs (roof, foundation, HVAC), and personal liability exposure. Successful investors mitigate these risks through adequate cash reserves (6-12 months expenses), proper insurance coverage (landlord policies, umbrella insurance), thorough due diligence including professional inspections, conservative financial projections assuming vacancies and repairs, and comprehensive tenant screening. Understanding that real estate is inherently a long-term investment that cycles through periods of growth and correction helps maintain perspective during market volatility and avoid panic-driven decisions.
Can I invest in real estate with my retirement account?
Yes, through self-directed IRAs that allow alternative investments including real estate. However, complex IRS rules prohibit self-dealing (you cannot personally benefit from IRA-owned properties), require proper administration through specialized custodians, and create complications around repairs and management. This approach works best for completely hands-off strategies like REIT investments, real estate crowdfunding, private lending to other investors, or turnkey rental properties with third-party management. Direct property ownership in self-directed IRAs requires careful compliance to avoid prohibited transactions that could disqualify the entire IRA. Consult with specialized self-directed IRA custodians and tax professionals before implementing this strategy to ensure full understanding of requirements and restrictions.
Important Disclaimer
No Financial, Investment, or Legal Advice: This article is provided for informational and educational purposes only and does not constitute financial, investment, tax, or legal advice. The real estate investment strategies, market data, and financial information discussed carry inherent risks, including the potential loss of principal invested.
Past Performance Not Indicative of Future Results: Historical returns, market performance data, and case studies presented do not guarantee similar future outcomes. Real estate markets are cyclical and subject to numerous economic, political, and local factors that can significantly impact investment performance.
Individual Results Will Vary: Success in real estate investing depends on numerous factors including but not limited to: individual effort and skill, market conditions, property selection, timing, financing terms, management quality, and economic factors beyond any investor’s control.
Consult Qualified Professionals: Before making any investment decisions or implementing any real estate strategies discussed in this article, you should consult with qualified financial advisors, tax professionals, real estate attorneys, and other experts appropriate to your specific situation. Laws, regulations, tax codes, and market conditions vary significantly by location and change over time.
No Guarantee of Accuracy: While we strive for accuracy, all market data, statistics, rates, and other information are subject to change and may contain errors or omissions. We make no warranties or guarantees regarding the accuracy, completeness, or timeliness of any information presented.
No Liability: The author, publisher, and Sezarr Overseas accept no responsibility or liability for any losses, damages, costs, or expenses (whether direct, indirect, consequential, or otherwise) arising from the use of, reliance upon, or implementation of any information, strategies, or recommendations contained in this article.
Do Your Own Due Diligence: Readers are solely responsible for conducting their own thorough due diligence, research, and analysis before making any investment decisions. Never invest money you cannot afford to lose.
Market Data Current as of: November 22, 2025. Real estate market conditions, mortgage rates, regulations, and other factors discussed are subject to rapid change.
About Sezarr Overseas: We provide comprehensive analysis and insights on investment strategies, emerging technologies, and market trends. For more expert content on building wealth and navigating financial markets, explore our resources on investment strategies, technology trends, and emerging market opportunities.